
How do you know you have Achilles tendinitis?
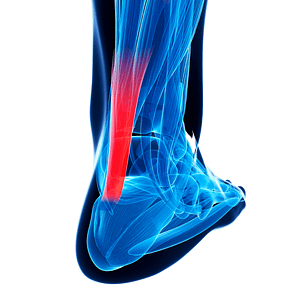
Table of Contents
What is Achilles tendinitis?
Achilles tendinitis is a common condition related to the tendon being overused, whether you’re going about your daily life or a serious athlete! Affecting both inactive and active individuals. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the heel bone. Being the strongest tendon in the body, it helps you walk, run, and jump by raising your heel off the ground. It also withstands stress from daily activities.
Achilles tendonitis is also known as inflammation of the Achilles tendon. This can occur during a sudden spurt of exercise due to not taking time the to warm up beforehand. Overtraining often can aggravate the tendon, especially when there has been little time for rest in-between exercise sessions.
What does Achilles tendinitis feel like?
The most common symptom will be the pain and stiffness along the calf muscle area, generally around the heel area. Mostly felt when you first get up in the morning. Another clue can be the increasing discomfort with pain towards the start and end of an activity such as running and brisk walking. The Achilles area will also be swollen and painful to touch. there will be a loss of function as it is responsible for the flexing of the foot. You may even struggle to move your foot up and down or lift your toes.
Who is at risk for Achilles tendinitis?
This type of injury can suddenly appear when participating in occasional recreational sports, especially if the sport involves quick stops and starts. Some bodies just aren’t used to the sudden action and stress on the tendon. There is a high incidence among active people. Avid athletes are prone to Achilles tendon injuries. Those involved in playing rugby and soccer have high incidence rates of Achilles tendon injuries so it is no surprise that it occurs more commonly in men.
Apart from causes from repetitive activity, there are also some other factors that can increase the risk of injury. Age is a factor especially for those 30 years and over due to wear and tear. Those with weak or tight calf muscles can be prone to injury. As people age, their tendons are easier to injure as they become less flexible.
Tendonitis from arthritis is more common in middle aged or older adults. A bone spur or growth may form in the back of the heel bone. The Achilles tendon gets affect by this and causes pain and swelling
Achilles tendinitis recovery and treatment
Sadly, there is no quick fix for this injury! Most cases of tendinitis can be treated with rest, physical therapy and medications to reduce pain. Resting is probably first and foremost one of the best treatments for Achilles tendinitis. Physical therapy that includes strengthening the tendon will assist in your recovery. Depending on how long you have had the condition, it could take anything from 6 weeks to 3-6 months to get back to pre-injury. The first port of call should be to get in touch with a healthcare provider. They will examine your foot and then be able to work out the best treatment plan, provide a strengthening program as well as monitor progress.
You can also contact a physiotherapist near you. They provide hands-on care to treat, restore normal function, and improve mobility. They will examine your condition and then be able to work out the best treatment plan, provide a strengthening program as well as monitor progress. Find a physiotherapist here
Delaying treatment can lead to a tendon tear
An inflamed Achilles tendon can be managed and treated in a reasonable time frame. However if you do nothing with your injury, it may even get worse and develop into a longer-term chronic problem.The tendon can become thicker and harder. Leaving it untreated can lead to an Achilles tendon rupture. This will probably lead to surgery for a repair, and a much longer time frame for recovery. It is much easier to treat this condition which is still manageable.
If you experience persistent pain around the Achilles tendon, call your doctor. Treating Achilles tendinitis in the early stages, will set you up for a better chance of success. You are likely to experience further problems down the line with possible complications by not treating your condition sooner rather than later. A great way to keep mobile during this time, while still resting your ankle would be to use a knee scooter. This device allows you to continue daily activities while still being able to be mobile.
